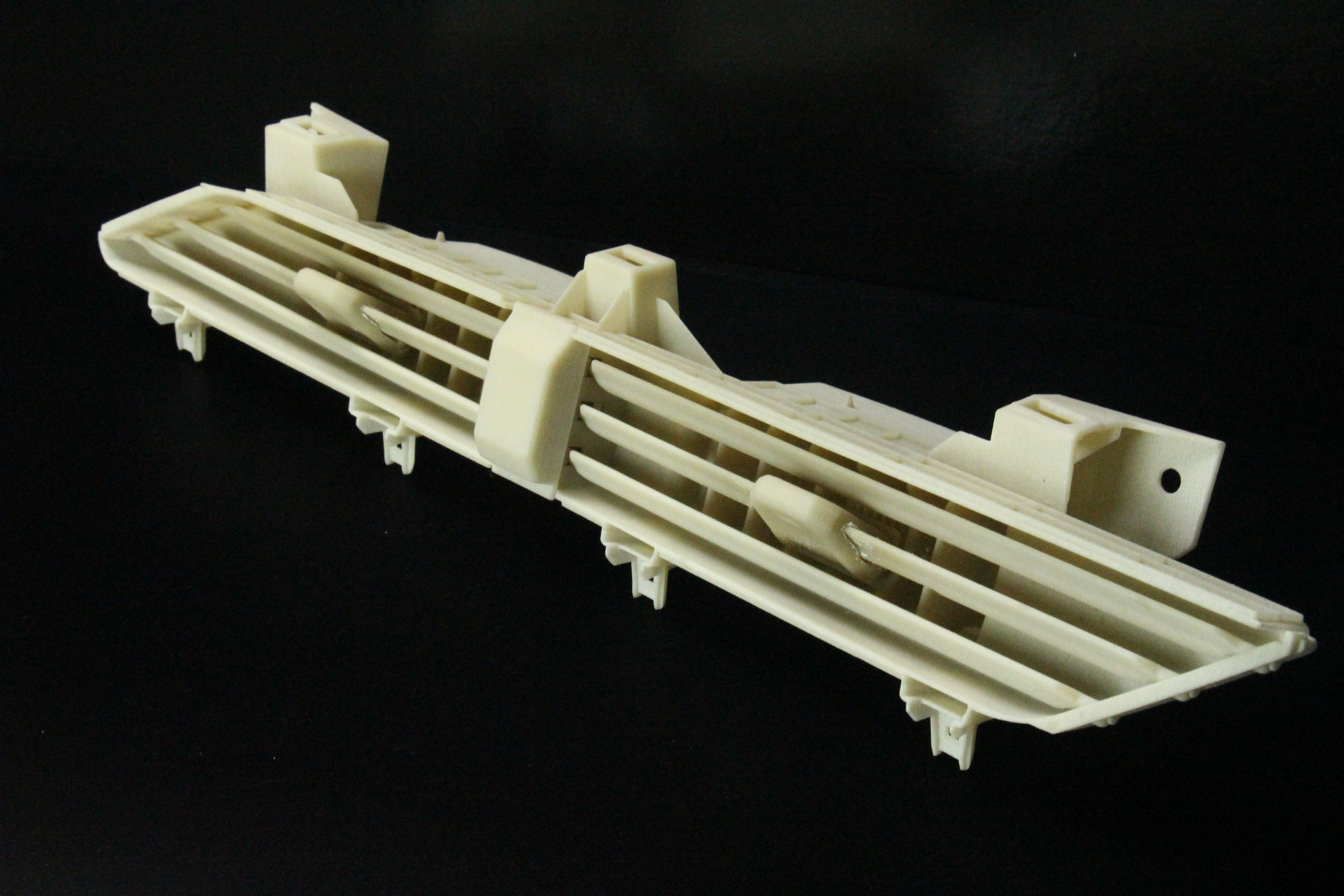
Additive Manufacturing
Witness your designs come to life layer by layer, as cutting-edge technology enables the creation of complex shapes with unmatched precision. From rapid prototyping to customized production, explore limitless possibilities and redefine what's possible with our advanced additive manufacturing.
aka 3D Printing
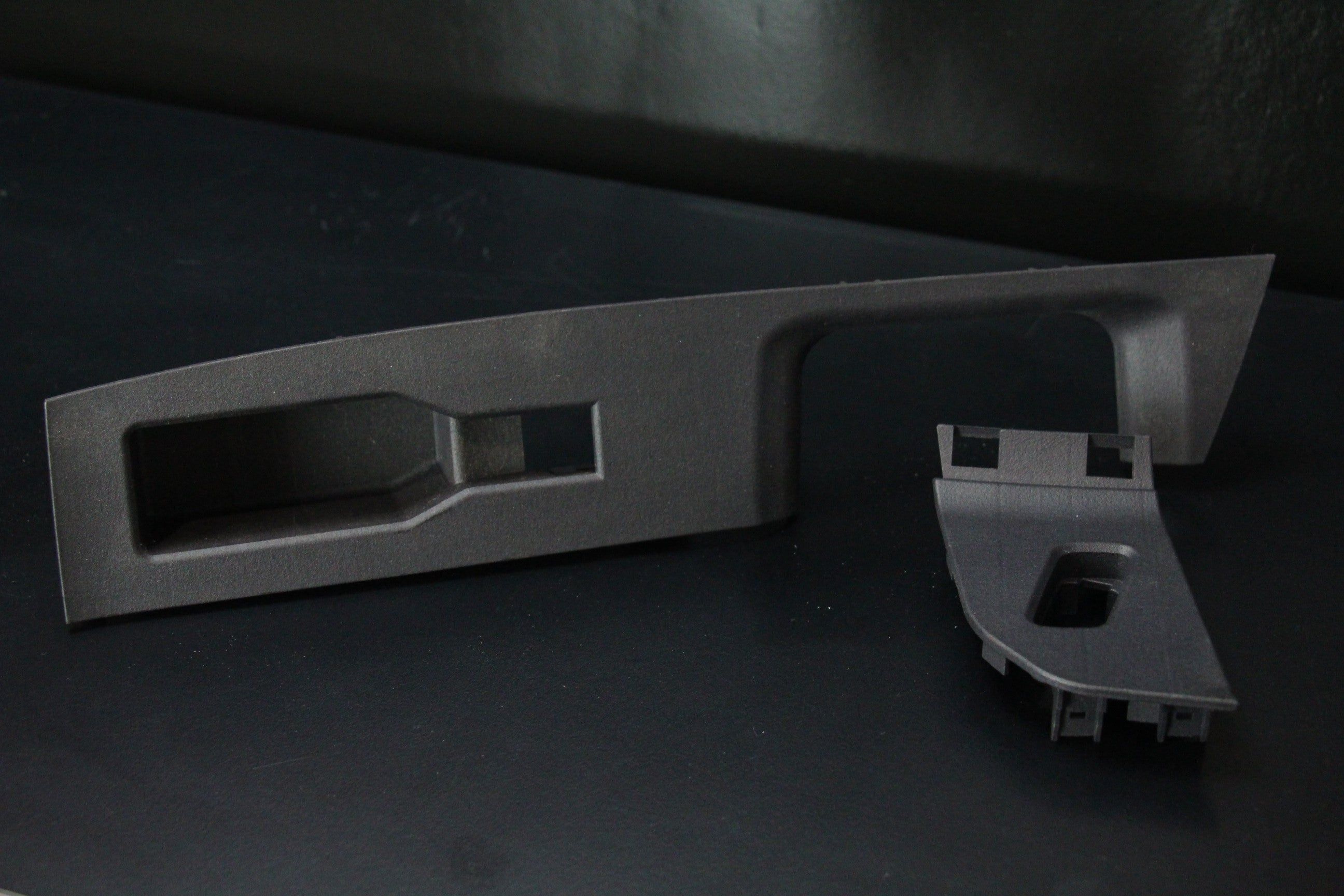
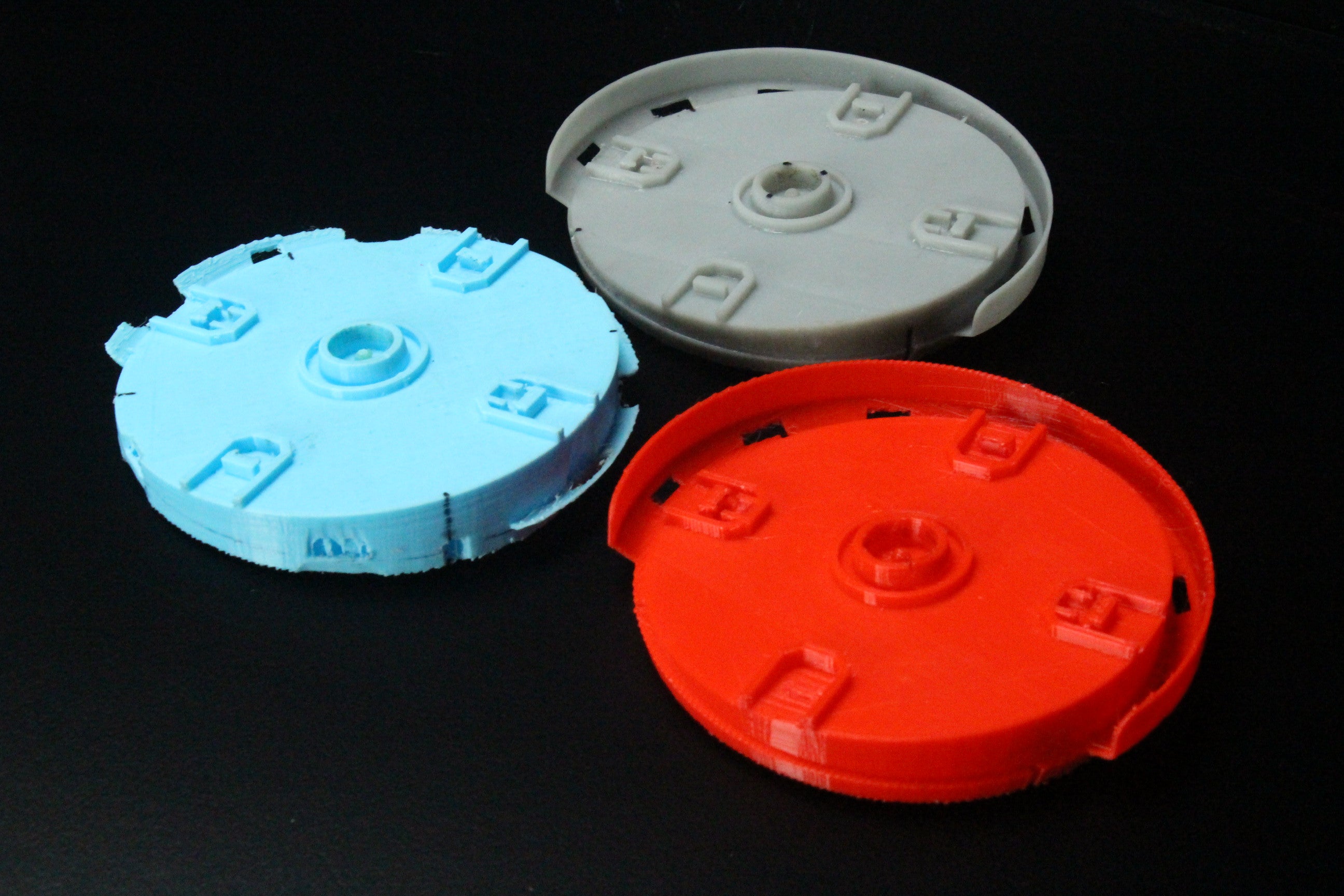
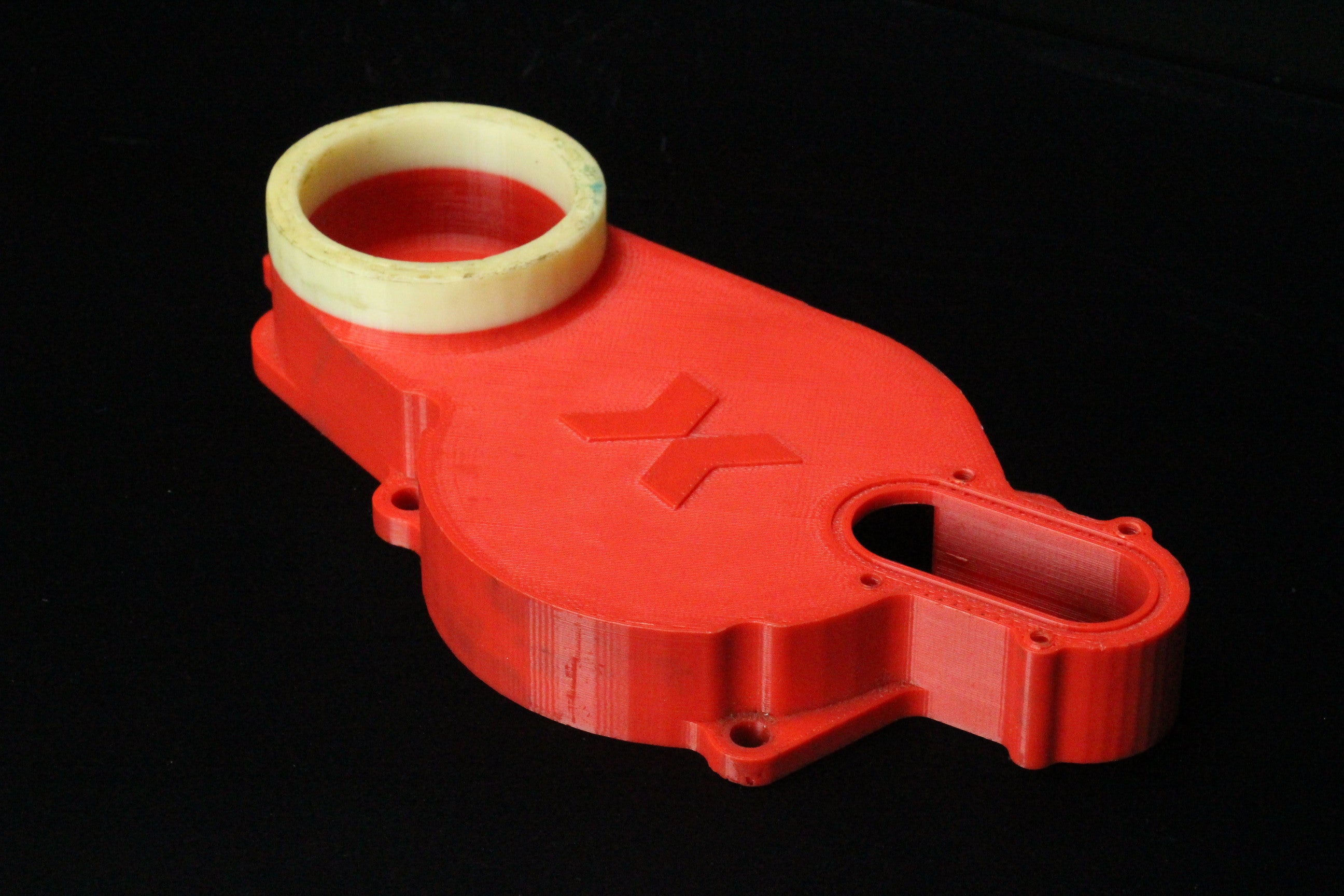
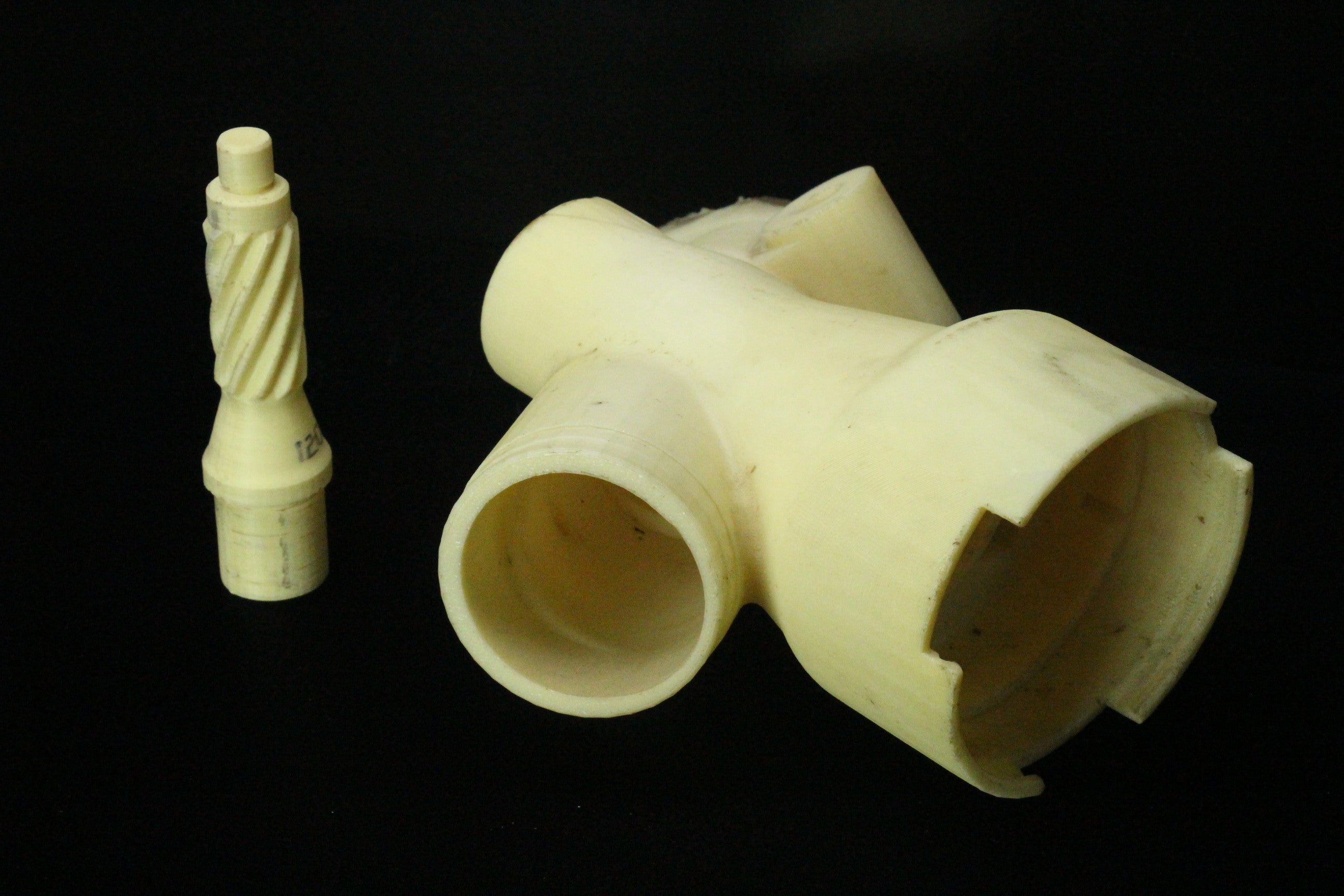
3D Printing is a revolutionary technology transforming the engineering landscape. This process involves creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital model. It allows for the production of designs that are often impossible or cost-prohibitive with traditional manufacturing methods.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Engineering
- Design Flexibility: Engineers can create complex parts without the constraints of traditional manufacturing. This capability enables the production of parts with optimized and improved performance characteristics.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing accelerates the prototyping phase, allowing engineers to quickly produce and test design iterations. This speed reduces time to market considerably.
- Cost Efficiency: By minimizing material waste and reducing the need for expensive molds and tooling, 3D printing can significantly lower production costs, especially for low-volume or custom parts.
- Customization: Additive manufacturing excels at producing customized parts tailored to specific requirements, making it ideal for bespoke engineering solutions and small batch productions.
- Supply Chain Simplification: 3D printing can produce parts on-demand, reducing the need for extensive inventory which simplifies logistics.
Applications in Engineering
- Prototyping and Testing: Our Engineers use 3D printing to create prototypes for testing and validation, ensuring designs meet specifications before full-scale production.
- Tooling and Fixtures: Custom tools, jigs, and fixtures can be printed to support manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
- End-Use Parts: This process is increasingly used for producing end-use parts, particularly in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries where lightweight and complex components are essential.
- Spare Parts and Repairs: 3D Printing allows our team to produce replacement parts quickly, reducing downtime and maintaining operational efficiency in various industrial settings.
Materials and Technologies
3D Printing encompasses various technologies, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each technology is compatible with different materials, such as plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites, offering a wide range of options for engineering applications.
Challenges and Considerations
While it offers numerous advantages, there are challenges to consider, such as material limitations, post-processing requirements, and the need for skilled operators. Engineers must evaluate these factors when integrating more advanced 3D Printing methods into their processes.
aka 3D Printing
3D Printing is a revolutionary technology transforming the engineering landscape. This process involves creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital model. It allows for the production of designs that are often impossible or cost-prohibitive with traditional manufacturing methods.
Benefits of 3D Printing in Engineering
- Design Flexibility: Engineers can create complex parts without the constraints of traditional manufacturing. This capability enables the production of parts with optimized and improved performance characteristics.
- Rapid Prototyping: 3D printing accelerates the prototyping phase, allowing engineers to quickly produce and test design iterations. This speed reduces time to market considerably.
- Cost Efficiency: By minimizing material waste and reducing the need for expensive molds and tooling, 3D printing can significantly lower production costs, especially for low-volume or custom parts.
- Customization: Additive manufacturing excels at producing customized parts tailored to specific requirements, making it ideal for bespoke engineering solutions and small batch productions.
- Supply Chain Simplification: 3D printing can produce parts on-demand, reducing the need for extensive inventory which simplifies logistics.
Applications in Engineering
- Prototyping and Testing: Our Engineers use 3D printing to create prototypes for testing and validation, ensuring designs meet specifications before full-scale production.
- Tooling and Fixtures: Custom tools, jigs, and fixtures can be printed to support manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
- End-Use Parts: This process is increasingly used for producing end-use parts, particularly in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries where lightweight and complex components are essential.
- Spare Parts and Repairs: 3D Printing allows our team to produce replacement parts quickly, reducing downtime and maintaining operational efficiency in various industrial settings.
Materials and Technologies
3D Printing encompasses various technologies, including Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). Each technology is compatible with different materials, such as plastics, metals, ceramics, and composites, offering a wide range of options for engineering applications.
Challenges and Considerations
While it offers numerous advantages, there are challenges to consider, such as material limitations, post-processing requirements, and the need for skilled operators. Engineers must evaluate these factors when integrating more advanced 3D Printing methods into their processes.